What is a Business Model Canvas?
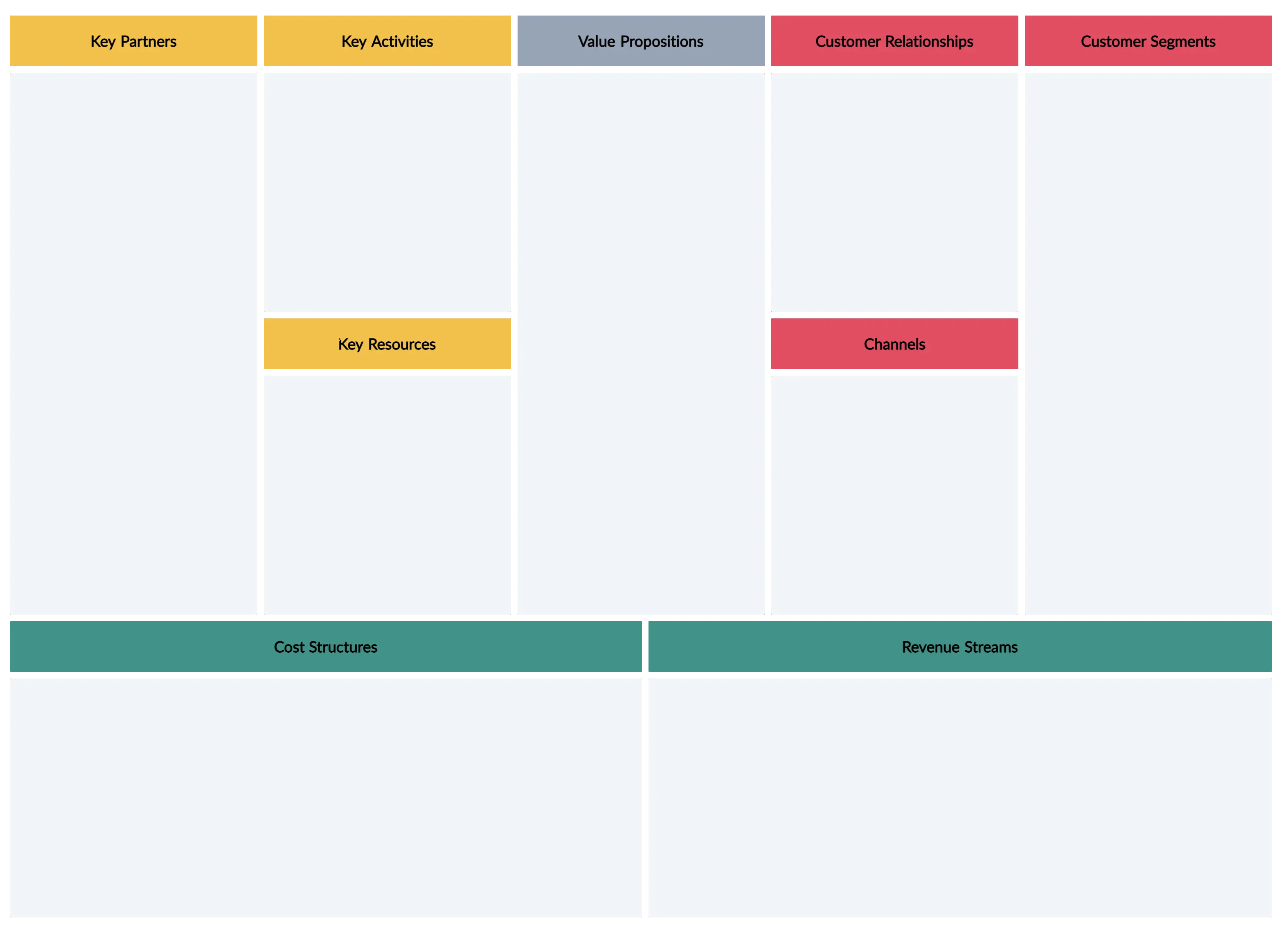
The Business Model Canvas is a one-page strategic tool that helps visualize and assess a business idea. It simplifies traditional business plans by breaking down nine key elements. The right side focuses on external, customer-related factors, the left on internal business operations, and the center highlights the value exchanged between the business and its customers.
How to Create a Business Model Canvas
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material
Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
Although you can create a business model canvas using whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using ready made business model canvas template allows you to access and update your work anytime, from anywhere.
Step 2: Set the context
Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas
Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks
Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas
Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate
Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize
Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
Components of a Business Canvas Model
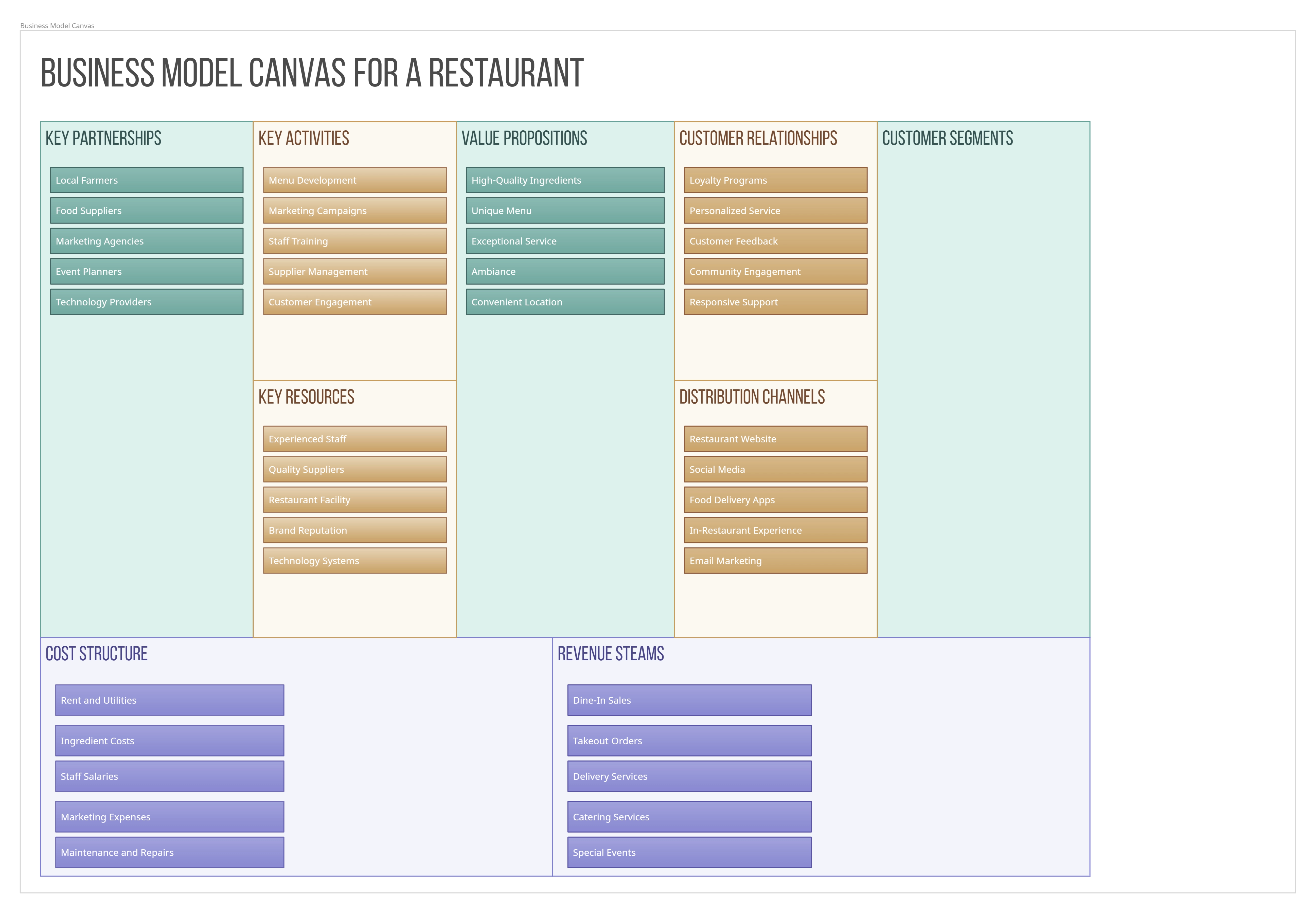
Customer Segments
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Different customer segments a business model can target;
- Mass market: This focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: This includes interdependent customer segments.
Customer Relationships
In this stage, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: You interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: Assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: Maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: This includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: tThese include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: Company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
Channels
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: Company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: Partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenue Streams
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: Made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: Made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: Selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: Charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: Charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
Key Activities
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: Designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: Finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
Key Resources
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key Partners
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: Partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: Strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: Partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: Ensure reliable supplies
Cost Structure
This section outlines all costs involved in running your business model. It includes expenses related to delivering value, generating revenue, and managing customer relationships.
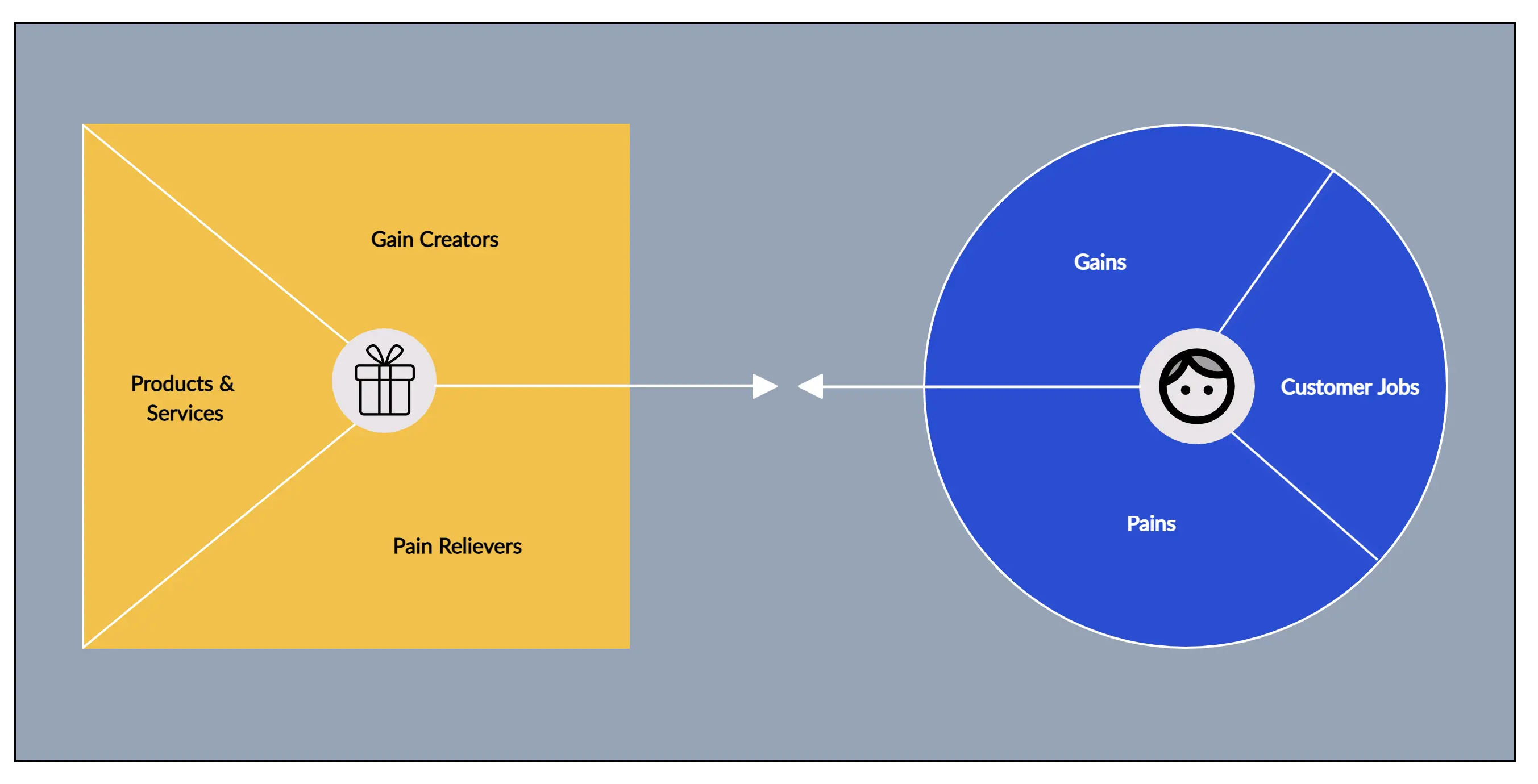
Value Propositions
The value proposition is the core of the Business Model Canvas, representing your unique product or service that solves a customer problem or creates value. It should stand out from competitors—either through innovation or unique features—and can be quantitative (like price or speed) or qualitative (like design or customer experience).
Free BMC Examples
FAQs About BMC
How do I determine my value proposition?
How can I build and maintain customer relationships?
What should I consider when establishing partnerships in the business model canvas?
How can the business model canvas help to analyze and optimize my business model?
Can I use the business model canvas for different types of businesses?
How often should the business canvas model be updated or revised?
How can I effectively communicate my business model to stakeholders using the business canvas model?
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
What are the benefits of using a business model canvas
What to avoid when creating a business model canvas
- Detailed financial projections
- Detailed operational processes
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies
- Legal or regulatory details
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements
- Irrelevant or extra information


Arjuna Fernando
Hi, I wish to learn more about Business model Canvas. How can I do that? Do you have any real world examples?