In this guide, we will explore effective decision-making techniques to help you make better decisions in various aspects of your life. Whether you’re facing personal dilemmas, professional challenges, or ethical quandaries, these techniques will provide you with the tools you need to navigate through any situation with confidence and clarity.
What is a Decision Making Technique?
A decision-making technique is a method or approach used to help people make better decisions. These techniques provide step-by-step processes or tools to consider options, weigh their pros and cons, and choose the best course of action. Examples include listing the advantages and disadvantages of each option, visualizing potential outcomes, or prioritizing based on key factors. These techniques help people make clearer, more informed decisions in different situations, like personal choices or business strategies.
6 Decision Making Techniques for Better Decisions
Here are 6 decision-making techniques that can be applied in various contexts, including personal decision-making, professional decision-making, strategic planning, problem-solving, and more. These techniques help individuals and organizations make better choices by providing structured approaches to analyze options, mitigate risks, and achieve desired outcomes.
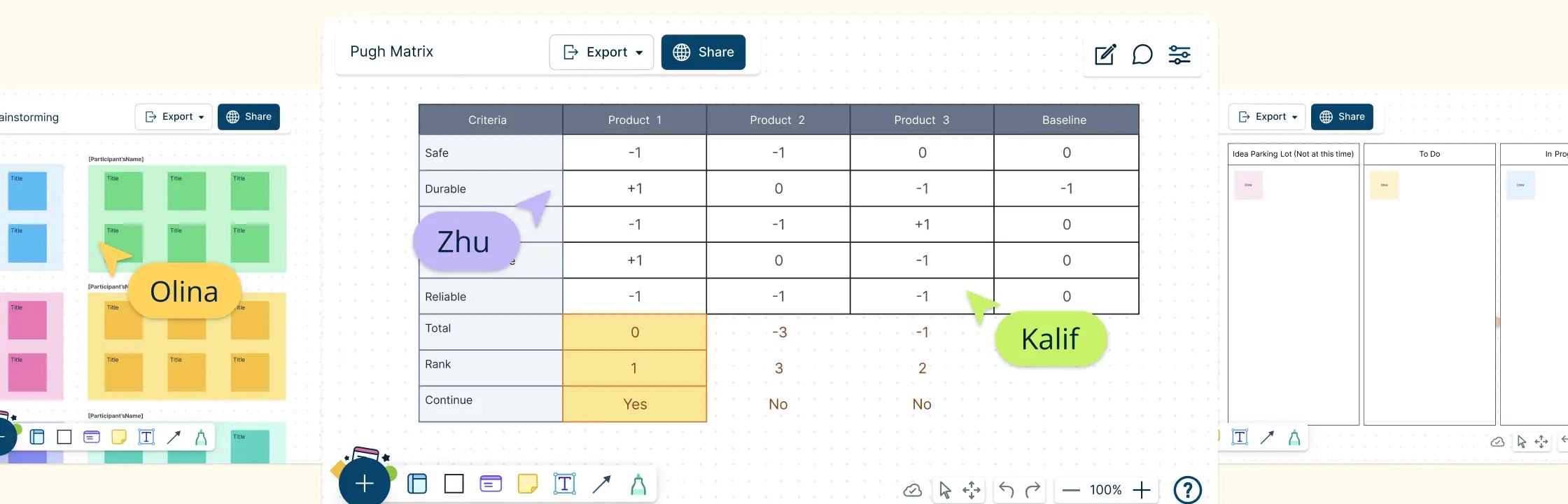
1. Pugh Matrix
What it is: The Pugh Matrix, also known as the Decision Matrix, is a structured technique for comparing multiple alternatives against a set of criteria. It helps objectively evaluate options by assigning scores based on predefined criteria.
How to use it in decision-making:
- Identify the decision to be made and the alternatives available.
- Determine the criteria for evaluation, such as cost, time, quality, etc.
- Assign weights to each criterion based on its importance.
- Compare each alternative against the criteria and assign scores.
- Calculate the total scores for each alternative to determine the best option.
Brainstorming
What it is: Brainstorming is a creative technique used to generate a large number of ideas or solutions to a problem in a short amount of time. It encourages free thinking and idea generation without criticism.
How to use it in decision making:
- Gather a group of participants with diverse backgrounds and perspectives.
- Clearly define the problem or decision to be addressed.
- Set a time limit and encourage participants to generate as many ideas as possible.
- Record all ideas without judgment or evaluation.
- After brainstorming, evaluate and refine the ideas generated to identify potential solutions.
The Heuristic Method
What it is: The heuristic method involves using practical rules or shortcuts to make decisions quickly, often in situations with limited information or time.
How to use it in decision making:
- Identify the decision to be made and any constraints or limitations.
- Use heuristics, or mental shortcuts, to simplify the decision-making process.
- Examples of heuristics include the “satisficing” approach (choosing the first option that meets the minimum criteria), the “availability heuristic” (relying on readily available information), or the “anchoring and adjustment heuristic” (starting with an initial estimate and adjusting based on new information).
Tiered Voting
What it is: Tiered voting is a decision-making technique where participants vote on options in multiple rounds, with the lowest-ranking options eliminated in each round until a consensus is reached.
How to use it in decision making:
- Present the options to be voted on to the participants.
- In the first round of voting, each participant ranks the options from best to worst.
- Eliminate the options with the lowest rankings and proceed to the next round of voting.
- Repeat the process until only one option remains, or until a predetermined threshold for consensus is reached.
SWOT Analysis
What it is: SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a decision, project, or organization.
How to use it in decision making:
- Identify the decision or project to be analyzed.
- List the internal Strengths and Weaknesses, such as resources, capabilities, or limitations.
- Identify external Opportunities and Threats, such as market trends, competition, or regulatory changes.
- Analyze the SWOT factors to inform decision-making and develop strategies to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and mitigate threats.
Game Theory
What it is: Game Theory is a mathematical framework used to analyze decision-making in situations where the outcomes depend on the choices of multiple parties, or “players.”
How to use it in decision making:
- Identify the decision or interaction involving multiple parties with conflicting interests.
- Define the players, their available strategies, and the possible outcomes.
- Use mathematical models to analyze the potential strategies and outcomes, considering factors such as payoff, risk, and utility.
- Determine the optimal strategy for each player, considering the potential responses of others, to achieve the best possible outcome or equilibrium.
Scenario Planning
What it is: Scenario planning is a technique used to make decisions in the face of uncertainty about the future. It involves creating multiple plausible future scenarios and analyzing their potential impact on the decision at hand.
How to use it in decision making:
- Identify the decision to be made and any uncertainties or future factors that could influence the outcome.
- Develop multiple scenarios, each depicting a different plausible future based on various combinations of key uncertainties.
- Evaluate each scenario’s potential impact on the decision, considering factors such as risks, opportunities, and challenges.
- Assess the robustness of the decision under each scenario and identify strategies to mitigate risks or capitalize on opportunities.
- Make the decision based on an understanding of how it would perform across different possible futures.
Priority Matrix
What it is: A Priority Matrix, also known as an Eisenhower Matrix or Urgent-Important Matrix, is a tool used to prioritize tasks or decisions based on their urgency and importance. It helps individuals or teams focus their efforts on the most critical tasks or decisions, thereby improving productivity and effectiveness.
How to use it in decision making:
- Identify the decisions or tasks that need to be prioritized.
- Create a prioritization grid with four quadrants: Urgent and Important, Important but Not Urgent, Urgent but Not Important, and Neither Urgent nor Important.
- Place each decision or task into one of the quadrants based on its level of urgency and importance.
- Focus on addressing tasks in the Urgent and Important quadrant first, as they require immediate attention.
- Delegate or schedule tasks in the Important but Not Urgent quadrant for later action, to prevent them from becoming urgent.
- Consider whether tasks in the Urgent but Not Important quadrant can be delegated or deferred, as they may distract from more critical priorities.
- Minimize or eliminate tasks in the Neither Urgent nor Important quadrant, as they contribute little value to achieving goals.
Conclusion
Effective decision making is a skill that can be honed through practice and awareness. By understanding the decision-making process, utilizing proven decision making techniques, and adapting to different contexts, you can navigate through life’s challenges with confidence and clarity. Remember, every decision you make shapes your future, so choose wisely.
Explore: