Are you struggling with bottlenecks in your work processes? Do you want to learn how to identify and resolve them effectively? If so, this blog post is for you!
What is a Bottleneck in a Process?
A bottleneck is a point in a process where the flow of work is slowed down or stopped by an obstacle or constraint. It can cause delays, waste, frustration and lower quality in your project outcomes. Bottlenecks can occur in any type of process, whether it is manufacturing, service, creative or administrative.
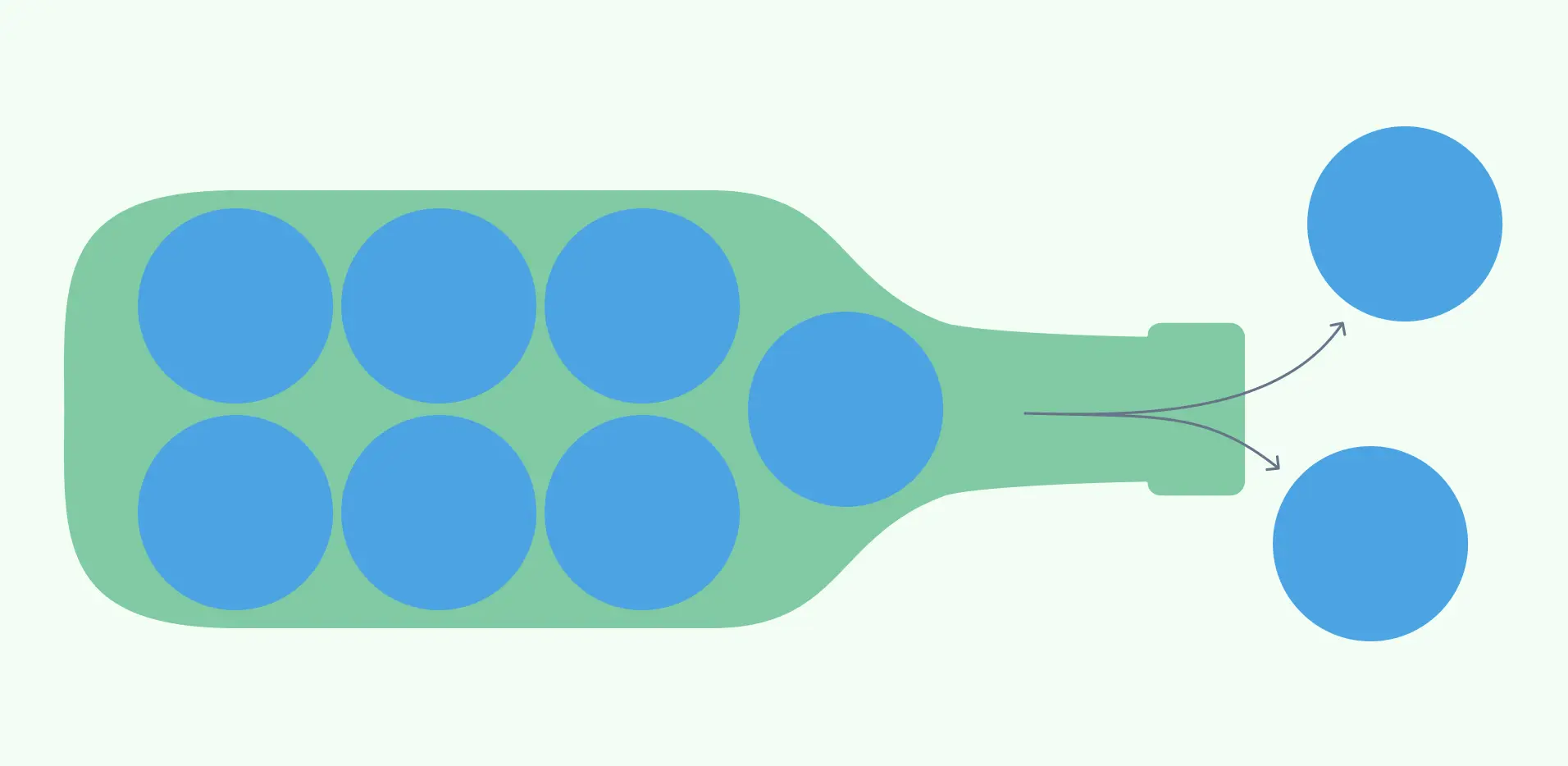
Some common examples of bottlenecks are:
- Slow approval process that delays the launch of a new product
- Limited budget that restricts the scope of a project
- High turnover rate that affects the continuity of a team
- Lack of feedback that hinders the improvement of a service
In this post, we will cover the following topics:
- How to Identify a Bottleneck in a Process
- Visual Frameworks to Identify Bottlenecks
- Types of Bottlenecks in Work Processes
- Techniques to Resolve a Bottleneck in the Process
- Wrapping Up
How to Identify a Bottleneck in a Process
There are several ways to identify the bottleneck in a process, such as:
- Analyzing the workflow and mapping out the steps involved
- Measuring the performance of each step and comparing it to the expected or desired output
- Identifying the sources of variation, errors, rework or waiting time in each step
- Asking for feedback from the stakeholders, customers or employees involved in the process
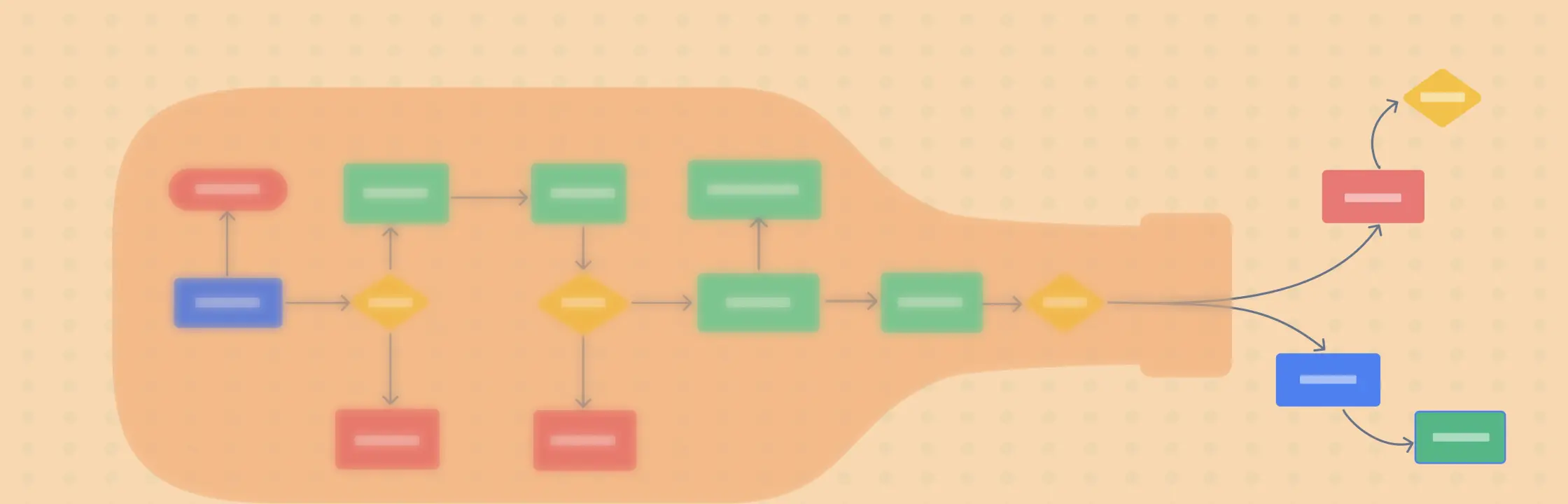
- Using tools such as Pareto charts, fishbone diagrams, flowcharts or value stream maps to visualize and analyze the process
Visual Frameworks to Identify Bottlenecks
The easiest way to identify a bottleneck is to visualize the process, and we have given a few visual frameworks that you can use for this.
Flowchart
Swimlane Diagram
Value Stream Map
Types of Bottlenecks in Work Processes
There are different types of bottlenecks that can affect your work processes, such as:
Resource bottlenecks: These occur when there is a lack of resources, such as people, equipment, materials or space, to complete a task or process. For example, if you have only one printer for a large team, it can create a bottleneck when everyone needs to print their documents.
Capacity bottlenecks: These occur when there is a mismatch between the demand and the supply of a task or process. For example, if you have more orders than you can fulfill, it can create a bottleneck in your production or delivery process.
Skill bottlenecks: These occur when there is a gap in the knowledge, skills or abilities of the people involved in a task or process. For example, if you have a complex task that requires specialized expertise, but you don’t have enough qualified staff to handle it, it can create a bottleneck in your project.
Communication bottlenecks: These occur when there is a breakdown or delay in the exchange of information, feedback or instructions among the people involved in a task or process. For example, if you have poor communication channels, unclear roles and responsibilities, or conflicting expectations among your team members, it can create a bottleneck in your collaboration.
Techniques to Resolve a Bottleneck in the Process
Once you have identified the type and cause of your bottleneck in the process, you can use various techniques to resolve it, such as:
- Eliminating or reducing the obstacle or constraint that is causing the bottleneck. For example, you can automate, outsource, delegate or streamline some tasks to free up resources or capacity. Use the 5 Whys Analysis and Fishbone diagrams to identify causes of bottlenecks.
Increasing or optimizing the resources or capacity that are needed for the bottleneck. For example, you can hire more staff, upgrade your equipment, acquire more materials or expand your space to meet the demand.
Improving or enhancing the skills or communication that are required for the bottleneck. For example, you can provide training, coaching, mentoring or feedback to your staff to improve their performance or collaboration.
Prioritizing or scheduling the tasks or processes that are affected by the bottleneck. For example, you can use tools such as Gantt charts, Kanban boards, Checklists
Wrapping Up
Bottlenecks are inevitable in any work process. However, they don’t have to be detrimental to your project success. By identifying and resolving them effectively, you can improve your productivity, quality of the project and customer satisfaction.
FAQs About Bottlenecks in Processes
How can I prevent bottlenecks from occurring in my work processes?
Some preventive measures that you can take are:
- Designing your work processes with flexibility and scalability in mind
- Setting realistic and achievable goals and expectations for your project
- Communicating clearly and frequently with your stakeholders and customers
- Monitoring and evaluating your work processes regularly and making adjustments as needed