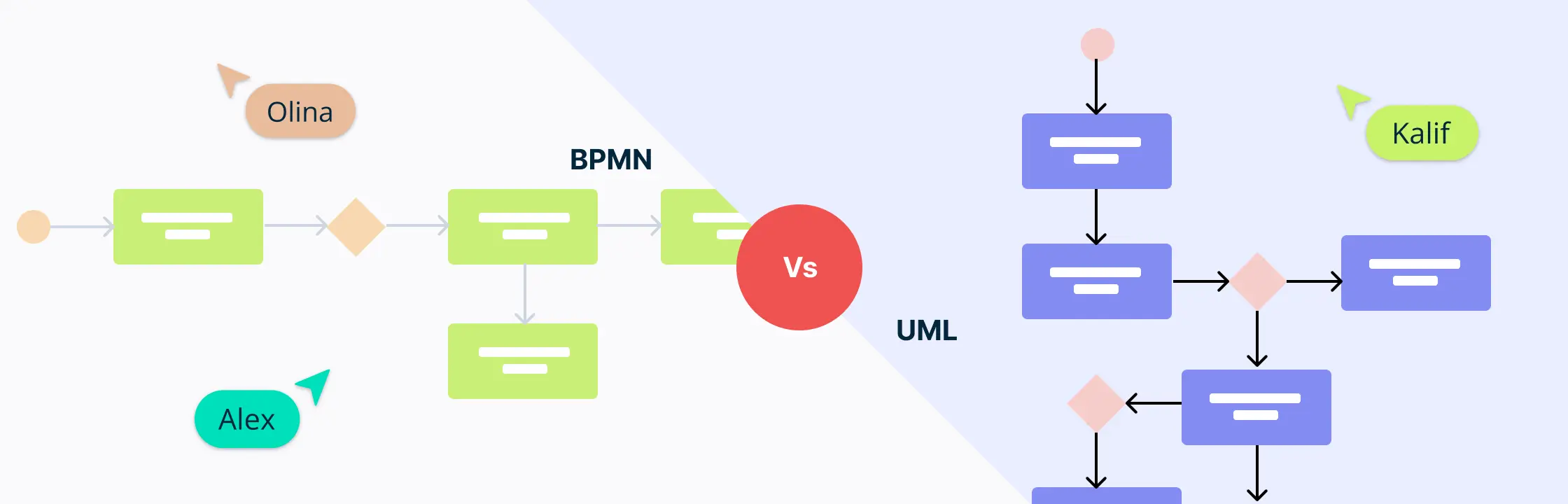
In business and tech, choosing between BPMN vs UML carries significant importance. If you are involved in process modeling, you know these languages are key to improving how organizations work. This short guide compares the basics of BPMN vs UML, helping you make smarter choices for your projects.
BPMN vs UML in Business Modeling
In business modeling, BPMN vs UML serve as handy tools, each with its unique strengths. BPMN gives organizations powerful tools for analyzing, optimizing, and illustrating processes. On the other hand, UML is an industry-standard tool for modeling complex software systems, helping with design and documentation throughout the development process.
BPMN in business modeling
BPMN provides a standardized visual language for representing and designing business processes. It helps organizations to map out workflows, identify process bottlenecks, and improve operational efficiency. BPMN’s clear and intuitive symbols make it easier for stakeholders to understand and communicate complex processes, promoting collaboration and ensuring a shared understanding of how business operations work. Additionally, BPMN is a key tool in business process mapping, enabling businesses to document and analyze their workflows for continuous improvement.
UML in business modeling
UML, or Unified Modeling Language, is a standardized modeling language used in software engineering to visualize a system’s architecture, design, and implementation. UML was originally developed for software engineering, but now it’s also used in business modeling, allowing you to represent organizational structures, behaviors, and interactions. Using UML, you can capture various aspects of a business, including its processes, roles, and information flow. In addition to offering a holistic view of the business context, it can also help with strategy planning, system design, and communication.
BPMN vs UML: Key Differences
While both BPMN vs UML are valuable modeling languages, they cater to different needs. Let’s take a look at how these two modeling languages are different from each other.
Here’s a table comparing example use cases for BPMN vs UML:
| Use Case | BPMN | UML |
|---|---|---|
| Business Process Improvement | Example: Mapping out a customer service process to identify inefficiencies and improve response time. | Not Ideal: UML focuses on software system design rather than process optimization. |
| Process Documentation for Compliance | Example: Documenting a workflow for a compliance audit, showing steps in approval and decision-making. | Not Ideal: UML is better suited for software modeling rather than business process documentation. |
| Software System Architecture | Not Ideal: BPMN is for business process mapping, not for detailed system architecture. | Example: Modeling system architecture and interactions for a new software application. |
| Process Communication to Stakeholders | Example: Using BPMN to present an easy-to-understand workflow for non-technical stakeholders in a project meeting. | Not Ideal: UML’s complexity makes it harder to convey process flows to non-technical audiences. |
| System Design & Behavior Modeling | Not Ideal: BPMN focuses on business processes, not system behaviors or structures. | Example: Modeling the behavior of a login system with state diagrams, sequence diagrams, and class diagrams. |
| Customer Journey Mapping | Example: Mapping out the steps in a customer’s interaction with a service from start to finish. | Not Ideal: UML does not provide specific tools for mapping customer journeys or business flows. |
Purpose and Focus in BPMN vs UML
BPMN: Primarily designed for business process modeling, BPMN focuses on visualizing and optimizing workflows. It uses standardized BPMN symbols to represent various elements in a business process, making it particularly effective for process documentation, analysis, and improvement.
UML: Developed for software engineering, UML has a broader scope. It encompasses a range of diagrams that can represent not only software systems but also organizational structures, behaviors, and interactions. UML is versatile and can be applied to various aspects of system design and modeling.
Application Domain in BPMN vs UML
BPMN: Suited for business process management and modeling. It excels in representing the flow of activities, decisions, and interactions within a business process.
UML: Applicable to software engineering and beyond. UML diagrams cover areas such as class structure, object interactions, state transitions, and more, making it versatile for various aspects of system modeling.
Level of Abstraction in BPMN vs UML
BPMN: Provides a high-level abstraction, emphasizing clarity and simplicity in depicting business processes. It is particularly useful for non-technical stakeholders.
UML: Offers a range of diagrams with varying levels of abstraction. While it can provide high-level overviews, UML is also capable of diving into detailed technical specifications, making it suitable for both technical and non-technical audiences.
Representation of Processes in BPMN vs UML
BPMN: Uses a set of standardized symbols (e.g., circles, rectangles, arrows) to represent events, tasks, gateways, and other elements in a process flow. This visual notation improves the understanding of business processes.
UML: Utilizes a variety of diagram types, such as activity diagrams and sequence diagrams, to represent different aspects of processes, interactions, and behaviors within a system. It provides a more comprehensive modeling approach beyond just process flow.
Primary Use Cases of BPMN vs UML
BPMN: Ideal for modeling and optimizing business processes. It is widely used in industries where visualizing workflows and improving operational efficiency are critical.
UML: Commonly employed in software engineering for system design and documentation. It is applied in various industries to model and communicate system structures, behaviors, and interactions.
BPMN vs UML: How to Choose the Right Modeling Language for Your Need
Choosing between BPMN vs UML depends on your modeling needs. Consider the specific objectives, audience, and nature of the system or processes you are modeling to determine which language aligns best with your requirements.
The following table compares BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) and UML (Unified Modeling Language) to help you decide which modeling language is best suited for your needs based on factors like purpose, audience, scope, and complexity. It provides a quick guide for choosing the right tool for business process management versus software system design.
| Criteria | Use BPMN | Use UML |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To model, analyze, and optimize business processes. | To design and document software systems, including their architecture, interactions, and behaviors. |
| Audience | Non-technical stakeholders (e.g., business managers, analysts) and those focused on process improvements. | Technical teams (e.g., software developers, architects, engineers) who require detailed system specifications. |
| Scope | Business process flows and their optimization. | Comprehensive modeling for systems that cover software, organizational structures, and more. |
| Level of Detail | High-level, abstract representation of workflows. | Both high-level overviews and detailed technical specifications for software development. |
| Modeling Focus | Primarily focused on business processes and workflow efficiency. | Covers various aspects of system design, including behavior, structure, and relationships. |
| Complexity | Best for visualizing processes in a simple, easy-to-understand format. | Best for modeling complex systems and components with diverse diagram types (e.g., class, sequence). |
| When to Use | - Modeling and optimizing business processes. | - Designing software systems. |
| - Communicating workflow changes to non-technical stakeholders. | - Documenting detailed system specifications for developers. |
Business Process Modeling
Choose BPMN if: Your primary objective is to model, analyze, and optimize business processes. BPMN is great for providing a standardized and visual representation of workflows, making it an ideal choice for activities related to business process management.
Software Engineering and System Design for BPMN vs UML
Choose UML if: Your modeling requirements go beyond business processes to include software engineering aspects, such as system architecture, class structures, and dynamic behaviors. UML offers a complete set of diagrams suitable for designing and documenting software systems.
Non-Technical Stakeholder Communication
Choose BPMN if: Your audience includes non-technical stakeholders, and you need a modeling language that is user-friendly and easy-to-understand. BPMN’s graphical notation system is designed to be easily understood by individuals with varying technical backgrounds.
Versatility and Diverse Modeling Needs
Choose UML if: Your modeling needs are diverse and may cover various aspects of a system, including software, organizational structures, interactions, and behaviors. Its adaptability makes it suitable for a variety of modeling scenarios.
High-Level Overview vs. Detailed Technical Specifications
Choose BPMN if: You prefer a high-level abstraction, focusing on straightforward representation of business processes. BPMN is particularly effective for providing a simplified overview of workflows.
Choose UML if: You need a modeling language that can cater to both high-level overviews for non-technical audiences and detailed technical specifications for developers and architects.
Specific Focus vs. Comprehensive Modeling
Choose BPMN if: Your modeling task is specifically centered around business processes, and you seek a specialized language tailored for this purpose.
Choose UML if: You anticipate a broader range of modeling requirements beyond business processes, including but not limited to software development, making UML a more comprehensive choice.
Helpful Resources
Visualize, analyze, and improve organizational processes on a single, connected workspace.
Fine-tuning your business process? Planning a project? Organizing your assignment? Whatever the situation, mind maps are a great way to visualize the process and execute it smoothly.
Use our powerful swimlane diagram maker to create business process diagrams online.
Identify waste and inefficiencies in your existing processes and collaborate to develop solutions for improvement using our advanced value stream mapping software.
Creately for Drawing UML and BPMN Diagrams
By leveraging a visual collaboration platform like Creately, you can easily create, collaborate, and share UML and BPMN diagrams.
Creately’s Advanced UML and BPMN Features
Advanced Modeling Capability
Creately offers advanced modeling capabilities that make it easier to manage and update your BPMN diagrams. With Creately, business process models are stored in a central database, ensuring that any update made to a process is reflected across all related process maps in real time. This centralized system allows for consistency and efficiency, ensuring that changes do not require manual updates to every individual diagram. As a result, you can update processes across multiple diagrams or views at once, making updates and changes to process maps much more manageable and scalable.
Create Live Maps
With Version History feature, Creately also enables the creation of live, dynamic BPMN maps that tracks updates in real time. Teams can collaborate simultaneously on the same map, ensuring that everyone is working with the latest version. This live map feature is invaluable for maintaining upto-date documents, ensuring correct information is available for enabling efficient analysis, decision-making, and collaboration.
Collaboration and Reusability
Creately allows seamless collaboration across teams with real-time updates, annotations, and contextual comments. The ability to reuse defined processes in multiple diagrams ensures that teams can maintain consistency across various projects without having to recreate diagrams from scratch.
Specialized Shape Libraries
Creately has comprehensive industry-standard shape libraries for bothe BPMN vs UML diagram types. Quickly drag and drop them on to the canvas and use Plus Create or Creately VIZ AI capabilities to draw or generate your diagram.
Real-Time Collaboration
Creately enable multiple users to work on UML and BPMN diagrams simultaneously, fostering real-time collaboration. Team members can contribute, discuss, and make changes in real time, improving overall productivity and teamwork. Add annotations, comments, and explanations directly onto the diagrams with contextual comments and use Spotlight on collaborators during presentations or discussions to follow them.
Pre-Made Templates
Creately offer pre-built templates and frameworks specifically designed for UML and BPMN, ensuring adherence to standardized symbols and notations. Streamline the diagram creation process, maintain consistency, and save time, especially for those new to the modeling languages.
Intuitive Interface and Drawing Tools
Creately has a user-friendly interface with a variety of drawing tools and shapes tailored for creating UML and BPMN diagrams. Easily design and customize diagrams, add elements like classes, activities, processes, and connectors effortlessly with the contextual toolbar and preset color themes.
Integrated Notes and Data
Keep everything related to your processes and systems in one place with notes and Shape data integrated to each shape. This makes it easy to add links and contextual details and attach documents or multimedia files and keep them in one spot for easy access and better organization.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between BPMN and UML allows users to choose the most appropriate modeling language based on their specific needs. Whether you are visualizing systems for developing software with UML or streamlining business processes with BPMN, each language brings its unique strengths to the table, helping you communicate, collaborate, and solve problems across domains effectively.