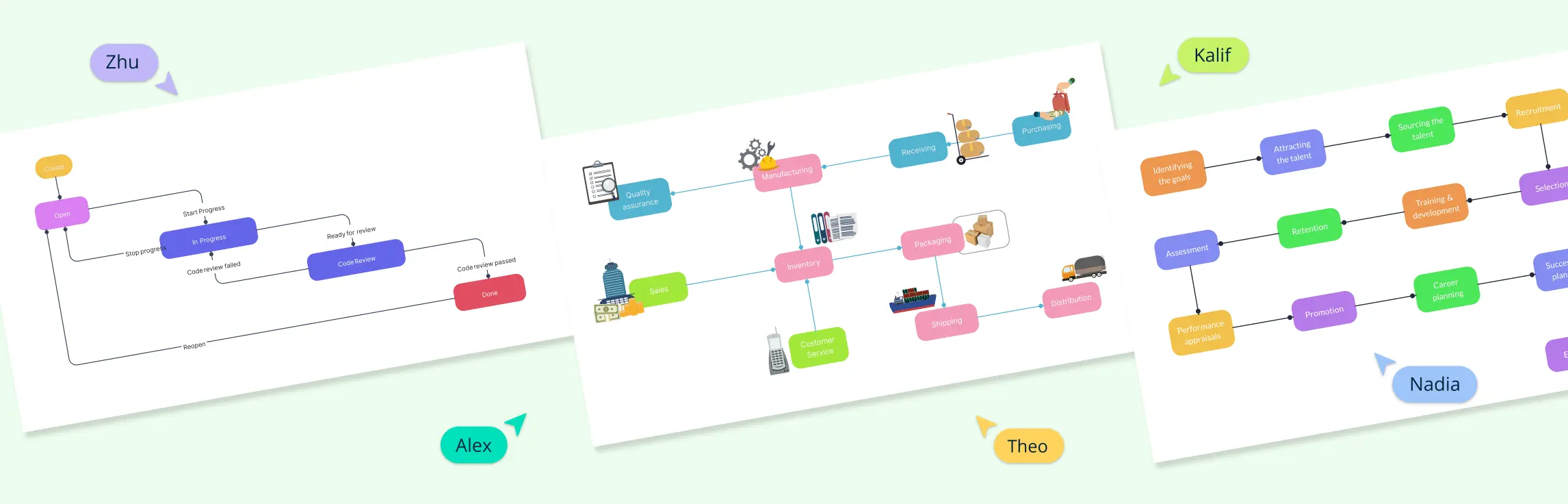
Why Business Process Mapping is Important
Businesses don’t just crop up overnight. Every objective is achieved through systematic processes. Business process modeling lets everyone from the heads of departments to concerned staff figure out the why, what, where and when of these processes. Process maps take all the data from here and present it visually.
The best establishments use business process maps to create visual representations of the inputs and steps that go into a service or end product. It’s easy to see why.
A process map is a visual representation of the concise sequence of tasks that are needed to bring a service or product from its conception to completion. A simplified, easy to understand representation of the processes to be resolved keeps everyone onboard aware of what needs to be done and what is expected of them to ensure it.
There are also a lot of misconceptions regarding business process mapping (BPM). A rundown of the key business process mapping best practices you need to know can help you use it more effectively to improve how you work.
5 Important Business Process Mapping Best Practices
Implementing effective business process mapping best practices is essential to streamline operations, improve team alignment, and enhance overall organizational performance.
Understand the Process Before Making Changes
Define Goals Beforehand
Recognize that It’s a Team Effort
Focus on Tasks that Drive Results
Don’t Forget to Follow Business Process Mapping Standards
Below is an expanded list of important best practices to ensure your business process maps are clear, actionable, and deliver results.
1. Understand the Process Before the Changes
No project is set in stone and will require modifications down the road. However, when creating a business process map, it is easy to get ahead of yourself and think of implementing possible changes before the tasks required for them even get off the ground.
If we wish to change something, we must understand it first. To do this in a process map, keep these thoughts in mind:
What is the process type? : The design of your business process map depends on the type of process it is for. Is it a management process like human resource management or organizational?
Who is in it? BPMs simplify and visualize complex tasks such as those that involve a lot of employees. Knowing who these people are can help define their responsibilities.
What are the tasks required? It’s not enough to know which tasks need to be executed. Also, determine their sequence to streamline them.
2. Goals Need to be Defined Beforehand
This kind of goes without saying. What is it that you want your business processes to achieve? Is it to solve a problem, train employees, create a product or ensure that it gets to a client?
To make the most of your BPM strategy, focus on goals by asking yourself:
What are the processes? To identify the relationship between the processes in your business process map, you need to identify what they are. For example, a goal of a supply chain process can be to expedite urgent deliveries.
Which processes should you map? Some goals have too many tasks and involve interactions with a lot of people. Taking a sequential approach to task management ensures that the tasks in your business process map are completed in a timely manner. But not all. Keeping simple tasks out of your map will keep it clutter free.
3. Understand that It is a Team Effort
Creating a business process map is one thing. Making changes in it, on the other hand, should be a team effort.
Implementing changes in it without thinking about the limitations and requirements of your team is a recipe for disaster. They need to be communicated, discussed and the final decisions need to be incorporated in the map.
There is a simple reason for this. The best way to keep employees engaged in a business process is to define their role in it, address and try to resolve any problems that might prevent them from carrying out their tasks efficiently.
For a business process model to be truly effective, it must acknowledge the unique challenges and streamline the tasks set out.
4. Focus on Tasks that Drive Results
The purpose of BPM is to map out tasks that need to be executed. However, while these tasks are no less important, the bottom line is to produce results.
Unfortunately, we get so focused on completing processes to the tee that we fail to consider whether they will actually bring desired results.
In other words, in a bid to create the perfect process map, we oftentimes forget why we use process mapping in the first place. To clear this up, focus on objectives and gear tasks in ways that makes achieving them easier for all parties involved. For example, ask yourself questions like:
What are the results that you are looking for?
What is it that you are trying to achieve and what are the tasks required for it?
5. Don’t Forget to Follow Business Process Mapping Best Practices and Standards
This is a very good chance that the objectives you want to achieve with your process maps have been achieved by someone else before. When starting out with business process mapping, following BPM techniques come in handy.
For example, a BPM best practice regarding process documentation is to not deviate from the value chain which is everything that contributes to the delivery of a product for instance. The chain should be represented in a way that clearly illustrates the products and the processes required to execute their delivery.
Here are some more business processes mapping best practices to keep in mind.
1. Define the purpose: Clearly define the purpose and objectives of the business process mapping exercise. Identify what specific outcomes or improvements you aim to achieve through the process mapping.
2. Start with high-level overview: Begin by mapping out the high-level steps or stages of the process before diving into the details. This helps to establish a clear structure and flow of the process.
3. Use visual symbols: Utilize standardized symbols and notation to represent different elements of the process, such as activities, decisions, inputs, outputs, and flows. This ensures consistency and improves readability.
4. Capture inputs and outputs: Clearly document the inputs and outputs at each step of the process. This helps to identify dependencies and ensures a complete understanding of the flow of information.
5. Include decision points: Identify decision points within the process where choices or alternate paths exist. Document the criteria for making decisions and the potential outcomes.
6. Validate and verify: Regularly review and validate the process maps with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. Seek feedback and incorporate any necessary revisions or improvements.
7. Focus on value-added activities: Identify and prioritize value-added activities within the process. This helps to streamline the process and eliminate non-value-added or redundant steps.
8. Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies: Look for bottlenecks, delays, or inefficiencies within the process. Use process mapping to pinpoint areas for improvement and redesign to enhance efficiency.
9. Consider automation opportunities: Assess the process maps for opportunities to automate certain tasks or activities. Identify areas where technology or tools can be utilized to streamline the process and improve productivity.
10. Incorporate Decision Points Clearly: Always include decision points in the map to illustrate where choices or alternate paths exist, along with the criteria used to make these decisions. This approach helps clarify process complexity and provides insights into potential outcomes.
11. Regularly Validate and Review the Process Map: Frequent validation and reviews are essential to maintain an accurate, effective process map. Stakeholders should regularly revisit the map, ensuring it still aligns with objectives and adjusting as needed.
12. Prioritize Value-Added Activities: Identify which activities directly contribute to the end goal and streamline or eliminate non-value-added tasks. This best practice helps keep the process efficient and focused.
13. Identify Bottlenecks and Consider Automation Opportunities: Use your business process mapping exercise to identify bottlenecks and redundancies that may slow down workflow. Where possible, look for automation opportunities to increase productivity, reduce errors, and streamline complex tasks.
By following these business process mapping best practices, teams can create clearer, more actionable maps that support organizational goals and make process improvement an ongoing initiative. Integrating best practices not only strengthens the effectiveness of each map but also contributes to a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Helpful Resources
Visualize, analyze, and improve organizational processes on a single, connected workspace.
Fine-tuning your business process? Planning a project? Organizing your assignment? Whatever the situation, mind maps are a great way to visualize the process and execute it smoothly.
Use our powerful swimlane diagram maker to create business process diagrams online.
Identify waste and inefficiencies in your existing processes and collaborate to develop solutions for improvement using our advanced value stream mapping software.
Avoiding Common Mistakes to Align with Business Process Mapping Best Practices
Here are additional business process mapping best practices that can enhance effectiveness and maximize the impact of your mapping efforts:
1. Involve Key Stakeholders Early
Ensuring that all relevant stakeholders are involved from the beginning is one of the most valuable business process mapping best practices. Their insights can clarify workflows, reveal hidden challenges, and create a shared commitment to the final process map.
2. Use Real-World Data for Accuracy
A critical business process mapping best practice is to base your mapping on real data instead of assumptions. This approach ensures that the process map accurately reflects actual workflows and identifies genuine bottlenecks.
3. Regularly Update Process Maps
Processes evolve over time, so it’s essential to update maps regularly. Regular review and updates keep the maps aligned with current practices, following business process mapping best practices for ongoing relevance and accuracy.
4. Limit Scope to Avoid Over-Complexity
To adhere to business process mapping best practices, keep each map focused on a single process or closely related activities. Avoid cramming multiple processes into one map, which can lead to over-complexity and reduced clarity.
5. Standardize Symbols and Terminology
Consistency in symbols, colors, and terminology across all maps is a fundamental business process mapping best practice. It reinforces clarity and makes it easy for anyone in the organization to understand any process map.
6. Incorporate Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
Embedding feedback mechanisms within the process map allows for continuous improvement. This business process mapping best practice ensures that inefficiencies are addressed as they arise, promoting ongoing optimization.
7. Utilize Digital Tools for Flexibility and Collaboration
Leveraging digital tools like Creately, is a valuable business process mapping best practice. These tools make it easy to update, share, and collaborate on process maps in real-time, encouraging a team-based approach to improvements.
8. Highlight Compliance Requirements
Mark parts of the process that fulfill compliance or regulatory requirements, following business process mapping best practices for clear and accessible maps. This helps teams stay aligned with critical legal or industry standards.
9. Document Lessons Learned
Each mapping exercise offers insights for future projects, and documenting these lessons is an important business process mapping best practice. This helps refine and improve the mapping approach over time.
10. Map Out Alternative Scenarios
Including alternative scenarios provides a comprehensive view of workflows and decision points. As one of the advanced business process mapping best practices, mapping variations ensures that maps are adaptable to different conditions.
Integrating these additional business process mapping best practices with foundational techniques will create process maps that are accurate, insightful, and aligned with your business goals, ensuring a robust and strategic approach to business process mapping.
Benefits of Business Process Mapping
Process understanding: Business process mapping provides a visual representation of workflows, enabling a clear understanding of how tasks, activities, and information flow within an organization.
Identification of inefficiencies: By mapping out processes, inefficiencies and bottlenecks can be identified and addressed, leading to improved productivity and cost savings.
Process standardization: Business process mapping facilitates standardization by defining consistent procedures and guidelines for performing tasks, ensuring consistency and quality across the organization.
Process improvement: Mapping out business processes allows for identification of areas for improvement, enabling organizations to streamline operations, reduce errors, and optimize resource allocation.
Cross-functional collaboration: Process mapping encourages collaboration and communication between different departments or teams involved in a process, fostering a shared understanding and alignment.
Risk management: By visualizing processes, potential risks and dependencies can be identified, allowing for proactive risk management and mitigation strategies.
Training and onboarding: Business process maps serve as valuable training and onboarding tools, providing new employees with a clear overview of how processes work within the organization.
Process automation: Business process mapping serves as a foundation for process automation initiatives, enabling organizations to identify areas suitable for automation and streamline operations.
Compliance and audit: Process mapping assists in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and facilitates audits by providing a documented overview of processes and controls.
Continuous improvement: Business process mapping promotes a culture of continuous improvement by facilitating ongoing evaluation and optimization of processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Advantages of Using Creately for Business Process Mapping
Creately offers a robust, feature-rich platform tailored to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and support both process and value stream mapping. Here are the standout features that make Creately an essential tool for effective business mapping:
1. Automatic Database Creation: With each element added to a process map, Creately builds a centralized database that links data across diagrams. Any change in one map reflects automatically in related maps, ensuring data consistency and enabling efficient process reuse.
2. Advanced Modeling Capabilities: Creately’s centralized storage model enables real-time updates across all maps, reducing manual adjustments and making long-term process management and scalability easier.
3. Dynamic “Living” Maps: Creately supports “living” process maps that evolve alongside changing business processes. Real-time updates, version control, and scheduled review sessions keep maps current, aligned, and reflective of actual business operations.
4. Real-Time Collaboration and Reusability: Shared workspaces allow team members to collaborate on process maps simultaneously, while process elements can be reused across projects for consistent workflows and reduced redundancy.
5. Customization and Data Integration: Extensive customization options and integrated data fields make process maps visually adaptable and contextually rich. Adding links, attachments, and data fields provides a well-organized, accessible resource.
6. Automation: Creately’s automation features, including diagram generation and bulk updates, simplify and speed up the process mapping experience, making it ideal for complex workflows or large-scale projects.
7. Real-Time Updates and Iteration: Built-in feedback mechanisms enable easy refinement of process maps, supporting continuous improvement initiatives and adaptation to new insights and business needs.
8. Template Library: A wide selection of templates designed for business mapping helps users adhere to best practices, ensuring rapid diagram creation and adherence to industry standards.
9. Workflow Optimization and Strategic Visualization: Creately’s visual tools support both incremental improvements and large-scale transformations, helping teams align process maps with strategic business goals and drive operational efficiency.
With these advanced features, Creately serves as a comprehensive platform for modeling, automating, and refining business processes. From process maps to value stream maps, Creately enables businesses to keep their workflows up-to-date and aligned with their latest goals and insights, making it an invaluable tool for optimizing operations and achieving strategic objectives.
Wrapping Up on Business Process Mapping
Every business objective needs to follow a process to ensure that it is executed in a timely manner. Business process mapping helps you understand all the processes involved in a project and achieve them with ease. Follow these business process mapping best practices to design effective work flows.
Author Bio
Farheen Shahzeb is a digital marketing expert and content strategist at Cygnis Media, an app development company that specializes in business intelligence (BI) software, enterprise web and mobile applications. An avid writer and researcher, she loves catching up on the latest trends and releases in BI tech.