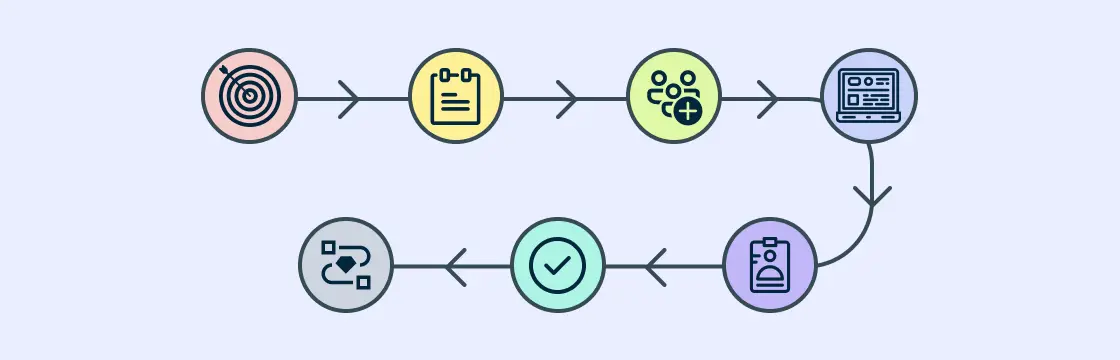
The recruitment life cycle, also known as full cycle recruiting encompasses the entire process of hiring a new employee, from identifying the need for a new hire to onboarding the selected candidate. This comprehensive process ensures that organizations attract, select, and retain the best talent available. Understanding the recruitment lifecycle is crucial for HR professionals and hiring managers as it provides a structured approach to managing the various stages of recruitment effectively.
Having a clear understanding of the recruitment lifecycle is essential for several reasons:
- Efficiency: A well-defined recruitment process helps streamline hiring activities, reducing time-to-hire and ensuring that the best candidates are not lost to competitors.
- Consistency: Standardizing the recruitment process ensures that all candidates are evaluated fairly and consistently, leading to better hiring decisions.
- Compliance: Adhering to a structured recruitment lifecycle helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements, minimizing the risk of legal issues.
- Candidate Experience: A smooth and transparent recruitment process enhances the candidate experience, improving the organization’s reputation and attracting top talent.
By understanding and implementing a structured recruitment lifecycle, organizations can achieve these benefits and more.
Full Cycle Recruiting: Stages of the Recruitment Life Cycle
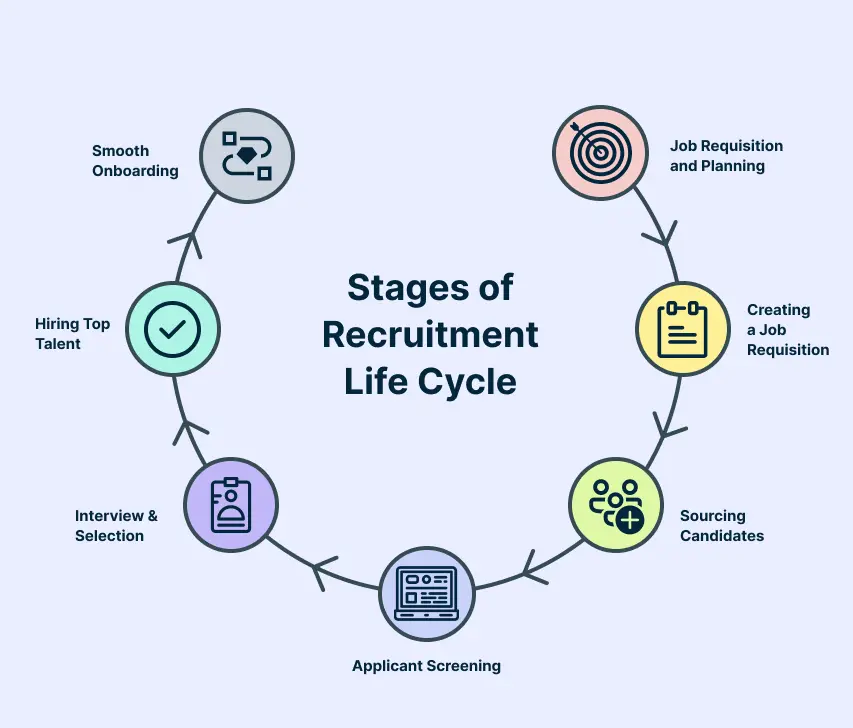
The recruitment lifecycle or full cycle recruiting is the end-to-end management of the recruitment process by a single recruiter or a dedicated team. This approach ensures consistency and accountability throughout the hiring process. This lifecycle consists of several key stages, each playing a vital role in the overall hiring process.
Each stage of the recruitment life cycle is interconnected, and a well-executed process ensures that the organization attracts, selects, and retains the best talent.
Stage 1: Job Requisition and Planning
Identifying Hiring Needs
The first step in the recruitment lifecycle is identifying the need for a new hire. This involves understanding the gaps in your current team and determining the skills and roles required to fill those gaps. Collaborate with department heads and team leaders to get a clear picture of the needs.
Creating a Job Requisition
Once the hiring needs are identified, the next step is to create a job requisition. A well-crafted job requisition ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page and helps streamline the recruitment process. Following are the essential details to be included in a job requisition.
Job Title: Clearly state the title of the position.
Department: Specify the department where the new hire will work.
Responsibilities: List the key responsibilities and tasks.
Qualifications: Detail the necessary skills and experience.
Budget: Include the salary range and any other financial considerations.
Set Recruitment Goals
Setting recruitment goals and timelines is also crucial. Define clear objectives for the hiring process, such as the number of candidates to interview and the desired start date. This helps in keeping the process on track and ensures timely hiring.
Collaboration with stakeholders is essential throughout this stage. Regular meetings and updates can help in aligning the recruitment strategy with the overall business goals.
Stage 2: Sourcing Candidates
Sourcing candidates is a critical stage in the recruitment lifecycle. It involves identifying and attracting potential candidates who fit the job requirements. Effective sourcing can significantly reduce the time-to-hire and improve the quality of hires. Here, we explore various strategies and tools to enhance your candidate sourcing efforts.
Identifying Sourcing Channels
There are multiple channels available for sourcing candidates, each with its unique advantages:
Job Boards: Platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, and Glassdoor are popular for posting job openings and reaching a broad audience.
Social Media: Leveraging social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter can help you connect with both active and passive candidates.
Employee Referrals: Encouraging current employees to refer candidates can lead to high-quality hires and improve employee engagement.
Recruitment Agencies: Partnering with agencies can provide access to a larger talent pool and specialized expertise.
Building and Maintaining a Talent Pipeline
Creating a talent pipeline ensures a steady flow of qualified candidates for future openings. Here are some steps to build and maintain an effective talent pipeline:
Identify Key Roles: Focus on critical positions that require a continuous supply of talent.
Engage Passive Candidates: Regularly interact with potential candidates who are not actively seeking new opportunities. Learn more about building a passive talent pipeline.
Utilize Recruitment Software: Tools like Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) can help manage candidate information and streamline the sourcing process.
Network Continuously: Attend industry events, webinars, and conferences to connect with potential candidates.
By leveraging these strategies and tools, you can enhance your sourcing efforts and build a robust talent pipeline. Additionally, using visual collaboration platforms like Creately can help HR teams visualize and streamline the entire recruitment lifecycle, making the process more efficient and effective.
Stage 3: Interviewing
Different Types of Interviews
Interviews are a critical component of the recruitment lifecycle, providing an opportunity to assess candidates’ skills, experience, and cultural fit. There are several types of interviews, each serving a unique purpose:
Structured Interviews: These follow a predetermined set of questions, ensuring consistency and fairness.
Unstructured Interviews: More conversational, allowing for a deeper exploration of the candidate’s background.
Behavioral Interviews: Focus on past experiences to predict future performance, often using the STAR method.
Panel Interviews: Multiple interviewers assess the candidate simultaneously, providing diverse perspectives.
Technical Interviews: Evaluate specific skills and knowledge relevant to the job role.
Preparation Tips for Interviewers
Effective preparation is key to conducting successful interviews. Here are some tips for interviewers:
Review Resumes: Thoroughly read the candidate’s resume to understand their background and experience.
Prepare Questions: Develop a mix of technical, behavioral, and situational questions.
Set the Environment: Ensure a quiet, comfortable space for the interview, whether in-person or virtual.
Practice Active Listening: Focus on the candidate’s responses, taking notes and asking follow-up questions as needed.
By following these tips, interviewers can create a structured and effective interview process, ensuring they gather the necessary information to make informed hiring decisions.
Stage 4: Selection and Offer
The selection and offer stage is a critical juncture in the recruitment lifecycle. This stage involves making the final decision on which candidate to hire, crafting a compelling job offer, negotiating terms, and extending the offer. Let’s delve into the key components of this stage.
Final Selection Process
After conducting thorough interviews and evaluations, it’s time to make the final selection. This involves:
Reviewing feedback from all interviewers
Comparing candidates against the job requirements
Assessing cultural fit and potential for growth
Making a consensus decision with the hiring team
Crafting a Compelling Job Offer
Once the final candidate is selected, the next step is to create a job offer that is both attractive and competitive. Key elements to include are:
Job title and description
Salary and benefits package
Start date and work schedule
Any additional perks or incentives
It’s essential to ensure that the offer aligns with industry standards and meets the candidate’s expectations.
Negotiating Terms
Negotiation is a natural part of the offer process. Be prepared to discuss:
Salary adjustments
Flexible work arrangements
Additional benefits or perks
Maintaining open communication and being flexible can help reach a mutually beneficial agreement.
Extending the Offer
Once terms are agreed upon, extend the formal offer. This can be done via email or a formal letter. Ensure that all details are clearly outlined and provide a timeline for the candidate to respond.
After extending the offer, be prepared for either acceptance or rejection. If the offer is accepted, initiate the onboarding process. If rejected, have a backup plan and consider other shortlisted candidates.
Stage 5: Onboarding
Onboarding is a critical stage in the recruitment lifecycle. It sets the tone for a new hire’s experience and can significantly impact their long-term success and retention within the company. Effective onboarding helps new employees acclimate to the company culture, understand their roles and responsibilities, and become productive members of the team more quickly.
Steps to Create an Effective Onboarding Plan
Pre-boarding: Start the onboarding process before the new hire’s first day. Send them necessary paperwork, company policies, and a welcome package to make them feel valued.
First Day Welcome: Ensure the new hire feels welcomed. Introduce them to their team, provide a tour of the office, and set up their workspace.
Training and Development: Provide comprehensive training sessions that cover job-specific skills, company tools, and processes. Utilize platforms like Creately to create visual training materials that are easy to understand and engaging.
Mentorship Programs: Pair new hires with experienced employees who can offer guidance and support during their initial months.
Regular Check-ins: Schedule regular check-ins to address any concerns, provide feedback, and ensure the new hire is settling in well.
Feedback Loop: Collect feedback from new hires about their onboarding experience to continuously improve the process.
For more detailed steps on creating an effective onboarding plan, you can read our guides on remote employee onboarding best practices and employee onboarding checklist.
Benefits of a Structured Recruitment Process
Implementing a structured recruitment process offers numerous benefits:
Improved Quality of Hire: A systematic approach to recruitment ensures that only the most qualified candidates are selected, leading to better job performance and reduced turnover.
Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitates better collaboration among HR teams, hiring managers, and other stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
Data-Driven Decisions: By documenting and analyzing each stage of the recruitment process, organizations can make data-driven decisions to continuously improve their hiring strategies.
Cost Savings: A streamlined recruitment process reduces the time and resources spent on hiring, leading to significant cost savings for the organization.
For more insights on optimizing your recruitment process for hybrid teams, check out our guide on the 7 step recruitment process.
Common Challenges in the Recruitment Lifecycle and Solutions
Recruitment is not without its challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
High Competition for Talent: Differentiate your employer brand and offer competitive benefits to attract top talent.
Time-Consuming Processes: Streamline your recruitment process using HR automation tools to manage workflows efficiently.
Unclear Job Descriptions: Ensure that job roles and responsibilities are clearly defined to attract the right candidates.
Poor Candidate Experience: Focus on improving communication and providing a seamless experience from application to onboarding.
Future Trends in Recruitment
The recruitment landscape is constantly evolving. Here are some future trends to watch out for:
AI and Automation: The use of AI in recruitment is set to increase, helping to automate repetitive tasks and provide data-driven insights.
Remote Work: With the rise of remote work, recruitment strategies will need to adapt to attract and manage remote talent effectively.
Diversity and Inclusion: There will be a greater focus on creating diverse and inclusive workplaces, impacting recruitment strategies and practices.
Data-Driven Recruitment: Leveraging data and analytics to make informed recruitment decisions will become increasingly important.
Wrapping Up
The recruitment lifecycle is a comprehensive process that involves multiple stages, each crucial for attracting, selecting, and retaining the best talent. From job requisition and planning to onboarding, understanding and optimizing each stage can significantly enhance your recruitment outcomes. A structured recruitment process not only ensures that you find the right candidates but also helps in maintaining a positive employer brand.
Mastering the recruitment lifecycle is essential for building a strong and capable workforce. By following best practices and leveraging advanced tools like Creately, HR teams can enhance their recruitment strategies and achieve better outcomes.